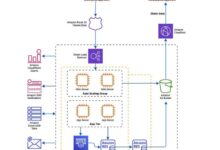
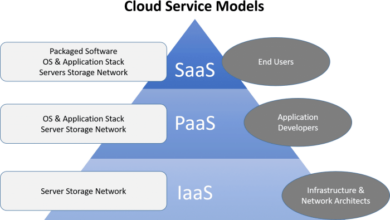
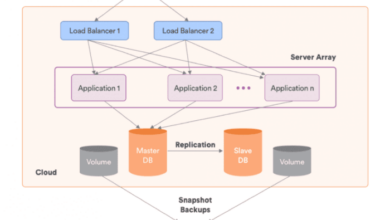
Unveiling Cost-Effective Cloud Architecture Diagrams: A Path to Optimal Resource Allocation
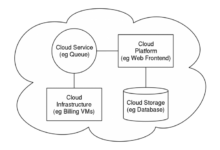
In the realm of cloud computing, optimizing costs while maintaining performance and scalability is a constant pursuit. Cloud architecture diagrams serve as blueprints for designing and managing cloud environments, and understanding how to leverage these diagrams for cost optimization is crucial.
This discussion delves into the fundamental principles, architectural patterns, resource management strategies, and tools that empower organizations to achieve cost efficiency in their cloud deployments.
The journey to cost optimization begins with grasping the core principles of cloud architecture, emphasizing the significance of selecting the right cloud provider and pricing model. By understanding the nuances of resource allocation, organizations can avoid overprovisioning and optimize resource utilization, leading to significant cost savings.
Cost Optimization Principles

In cloud architecture, cost optimization involves leveraging strategies and techniques to minimize cloud computing expenses while maintaining performance and reliability. The core principles of cloud architecture for cost optimization include:
- Selecting the Right Cloud Provider and Pricing Model: Choosing a cloud provider that aligns with your organization’s needs and selecting the most suitable pricing model can significantly impact costs.
- Rightsizing Resources: Avoiding overprovisioning and ensuring resources are appropriately sized to match actual usage patterns helps prevent unnecessary costs.
- Using Cloud-Native Tools and Services: Leveraging cloud-native tools and services designed for cost optimization can provide valuable insights and automation.
- Optimizing Performance and Efficiency: Implementing performance optimizations and resource efficiency techniques can reduce costs associated with underutilized or inefficient resources.
Rightsizing Resources
Rightsizing resources involves carefully allocating and managing cloud resources to match actual usage patterns and requirements. This approach helps avoid overprovisioning, where resources exceed actual needs, leading to higher costs. Effective rightsizing involves:
- Monitoring and Analysis: Continuously monitoring resource usage patterns and analyzing performance metrics helps identify underutilized or overutilized resources.
- Scaling Strategies: Implementing autoscaling policies or manual scaling adjustments based on usage patterns can ensure resources are dynamically adjusted to meet fluctuating demands.
- Resource Allocation Strategies: Utilizing techniques like bin packing algorithms or resource pools can optimize resource allocation and minimize resource fragmentation.
- Rightsizing Tools: Leveraging cloud-native tools or third-party solutions specifically designed for resource optimization can automate and simplify the rightsizing process.
Architectural Patterns for Cost Efficiency
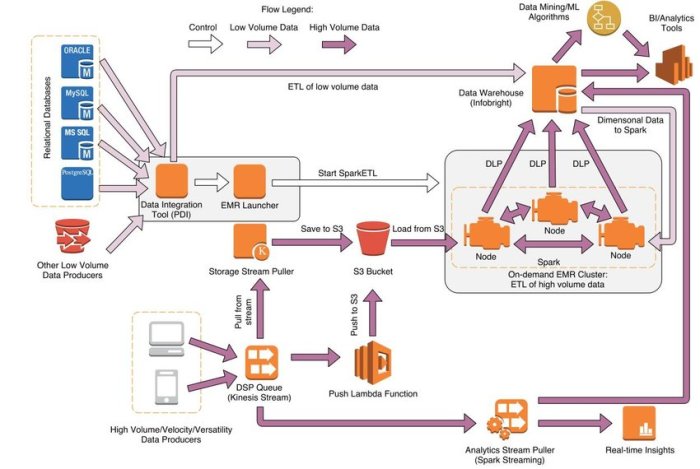
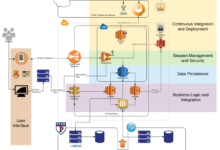
Adopting cloud-based architectural patterns can significantly optimize cost efficiency. This section explores various patterns, their benefits, trade-offs, and suitability for specific applications. Microservices Architecture Microservices decompose an application into a collection of loosely coupled, independent services. This pattern enables scalability, agility, and resilience.
Benefits:
- Improved cost efficiency through fine-grained resource allocation and optimization.
- Flexibility to scale individual services without affecting others.
- Reduced maintenance costs due to modularity and independent deployments.
Trade-offs:
- Increased complexity in development and management due to distributed systems.
- Potential for higher operational costs due to increased number of services.
Serverless Architecture Serverless computing abstracts away the need for managing infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on code execution without worrying about servers or resources. Benefits:
- Pay-per-use pricing model leads to significant cost savings.
- Scalability and elasticity without the need for capacity planning.
- Reduced operational overhead and maintenance costs.
Trade-offs:
- Limited control over infrastructure and resource allocation.
- Potential vendor lock-in if not carefully managed.
- Challenges in debugging and monitoring due to the lack of direct access to servers.
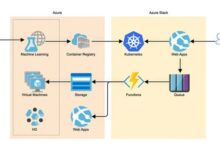
Multi-Cloud Architecture Multi-cloud involves using multiple cloud providers or platforms for different workloads or applications. This pattern helps optimize costs and reduce vendor lock-in. Benefits:
- Cost optimization by leveraging the strengths and pricing models of different cloud providers.
- Reduced risk of outages or disruptions by distributing workloads across multiple clouds.
- Improved flexibility and agility in managing and scaling applications.
Trade-offs:
- Increased complexity in managing multiple cloud platforms and services.
- Potential challenges in data integration and governance across different clouds.
- Risk of vendor lock-in if not carefully managed.
Choosing the Right Pattern The selection of the most suitable architectural pattern depends on various factors, including:
Application requirements
Consider the scalability, performance, and availability needs of the application.
Cost considerations
Evaluate the cost implications of each pattern, including infrastructure, maintenance, and operational costs.
Technical expertise
Assess the team’s capabilities and experience in managing and maintaining the chosen pattern.
Long-term goals
Consider the organization’s future growth plans and the scalability of the chosen pattern.
Cloud Resource Management Strategies
Effective cloud resource management is a critical aspect of cost optimization. Implementing sound strategies for resource tagging and labeling, monitoring and tracking resource usage, and establishing cost allocation and chargeback mechanisms can help organizations optimize their cloud spending and improve resource utilization.
Resource Tagging and Labeling
Assigning tags and labels to cloud resources enables organizations to categorize and organize their resources for better visibility and control. This practice facilitates the identification of resources associated with specific projects, departments, or applications, allowing for targeted cost analysis and optimization efforts.
Monitoring and Tracking Resource Usage
Regular monitoring of cloud resource usage is essential for identifying underutilized or overprovisioned resources. By leveraging cloud provider tools and third-party monitoring solutions, organizations can gain insights into resource utilization patterns, identify idle or inefficient resources, and adjust resource allocation accordingly.
Cost Allocation and Chargeback Mechanisms
Implementing cost allocation and chargeback mechanisms enables organizations to distribute cloud costs fairly and accurately among different business units or projects. This practice promotes accountability, encourages responsible resource consumption, and helps organizations make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and budgeting.
Tools and Techniques for Cost Analysis
To optimize cloud costs effectively, it is essential to leverage the right tools and techniques that provide visibility, analytics, and actionable insights into cloud spending. These tools empower organizations to make informed decisions, identify cost inefficiencies, and implement cost-saving measures.
One of the most crucial aspects of cost optimization is cost visibility. Cloud cost optimization tools provide detailed reports and visualizations that enable organizations to track cloud usage, costs, and trends over time. This visibility allows organizations to identify areas where costs can be reduced, such as underutilized resources, idle instances, or excessive usage of expensive services.
Cost Analysis Tools and Platforms
There are numerous cloud cost optimization tools and platforms available, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities. Some popular options include:
- Cloud Cost Management Tools: These tools, such as AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Cost Management, provide comprehensive cost visibility and analysis capabilities. They allow organizations to track costs across different cloud services, projects, and accounts, and identify cost anomalies and trends.
- Cloud FinOps Platforms: Cloud FinOps platforms, such as CloudHealth by VMware, Apptio Cloudability, and Flexera Cloud Cost Management, offer a comprehensive suite of tools and features for cloud cost optimization. These platforms provide detailed cost visibility, analytics, and recommendations for cost optimization, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and reduce cloud costs.
- Cloud Cost Monitoring and Alerting Tools: These tools, such as Datadog, New Relic, and CloudWatch, provide real-time monitoring of cloud usage and costs. They allow organizations to set cost alerts and notifications to identify and address cost inefficiencies promptly.
Importance of Cost Visibility and Analytics
Cost visibility and analytics play a critical role in informed decision-making and cost optimization. By leveraging cost analysis tools, organizations can:
- Identify Cost Drivers: Understand which cloud services, projects, or accounts are driving the majority of costs.
- Analyze Cost Trends: Track cloud costs over time to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential areas for cost reduction.
- Detect Cost Inefficiencies: Identify underutilized resources, idle instances, excessive usage of expensive services, and other inefficiencies that can be addressed to reduce costs.
- Forecast Future Costs: Use historical data and trends to forecast future cloud costs and plan accordingly.
Using Cost Reports and Alerts
Cost reports and alerts are powerful tools for identifying and addressing cost inefficiencies. Organizations can:
- Generate Cost Reports: Create detailed cost reports that provide insights into cloud usage, costs, and trends. These reports can be customized to include specific metrics, dimensions, and time periods.
- Set Cost Alerts: Configure cost alerts to notify organizations when cloud costs exceed predefined thresholds or when specific cost anomalies are detected. This allows organizations to respond promptly to cost inefficiencies and take corrective actions.
Continuous Optimization and Best Practices
Cost optimization in cloud architecture is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, analysis, and refinement. Adopting a proactive approach to cost management ensures that your cloud infrastructure remains efficient and cost-effective over time.
There are several best practices to follow for ongoing cost management:
Regular Reviews and Audits
Conduct regular reviews of your cloud architecture and resource usage to identify areas for improvement. This includes analyzing usage patterns, identifying underutilized resources, and evaluating the cost-effectiveness of your current architecture.
Architectural Refactoring
Periodically refactor your cloud architecture to improve efficiency and reduce costs. This may involve migrating to more cost-effective instance types, optimizing resource allocation, or implementing architectural patterns that are designed for cost optimization.
Automation
Automate as many cost management tasks as possible. This includes setting up automated alerts for cost overruns, implementing automated scaling policies, and using tools that can automatically optimize resource allocation.
Stay Updated with Industry Trends
Keep yourself updated with the latest cost optimization techniques and industry trends. This includes reading blogs, attending conferences, and following industry experts on social media.
Last Recap
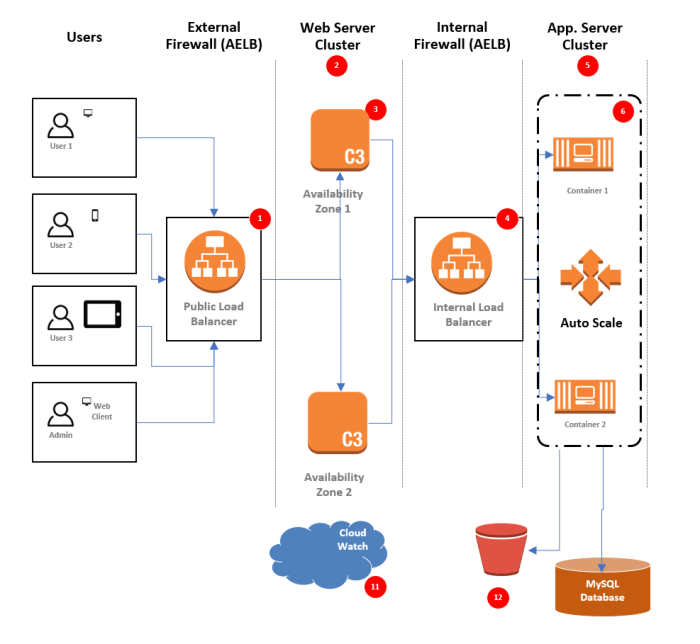
In conclusion, cloud architecture diagrams are indispensable tools for organizations seeking to optimize costs in their cloud environments. By adhering to fundamental principles, leveraging cost-effective architectural patterns, implementing resource management strategies, and utilizing cost analysis tools, organizations can achieve significant savings while maintaining the performance and scalability required for success in the digital age.