Deciphering Cloud Architecture Diagrams for Compliance: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital landscape, cloud computing has become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, with the proliferation of sensitive data stored in the cloud, organizations must navigate a complex web of compliance regulations and standards to ensure data security and privacy.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of cloud architecture diagrams for compliance, providing a visual roadmap for organizations to design and implement cloud architectures that adhere to regulatory requirements. By understanding the shared responsibility model, fundamental design principles, and key components of compliance-focused cloud architecture diagrams, organizations can effectively mitigate risks, protect sensitive data, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Compliance Regulations and Standards
Organizations operating in the digital landscape must adhere to a plethora of compliance regulations and standards to ensure the protection of sensitive data and maintain trust with their stakeholders. These regulations and standards provide a structured framework for organizations to design and implement secure cloud architectures that meet regulatory requirements.
Among the prominent compliance regulations and standards are:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation enforced in the European Union (EU) that governs the collection, processing, and transfer of personal data. It mandates organizations to implement robust security measures to safeguard personal data and grant individuals control over their data.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA is a US federal law that sets forth specific requirements for the protection of health information. Healthcare organizations and their business associates must comply with HIPAA regulations to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information (PHI).
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS is a set of security standards developed by the payment card industry to protect cardholder data during payment transactions. Organizations that process, store, or transmit cardholder data must adhere to PCI DSS requirements to maintain compliance and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001/27002: ISO 27001 is an information security management system (ISMS) standard that provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, and maintain an effective information security program. ISO 27002 is a supporting standard that offers guidance on implementing ISO 27001 requirements and best practices for information security controls.
These regulations and standards have a significant impact on cloud architecture. Organizations must consider compliance requirements when designing and implementing their cloud solutions to ensure adherence to regulatory mandates. Compliance-driven cloud architectures incorporate security controls, data protection mechanisms, and governance policies that align with regulatory requirements, enabling organizations to operate in a compliant and secure manner.
Shared Responsibility Model
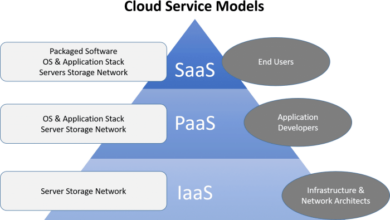
Cloud computing operates under the shared responsibility model, where cloud providers and customers have distinct roles in ensuring compliance.
The division of responsibilities between cloud providers and customers varies depending on the specific cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and the cloud provider’s policies. However, some general principles apply.
Security of the Cloud
Cloud providers are responsible for securing the infrastructure and platforms they provide, including physical security, network security, and operating system security.
Customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and workloads running on the cloud platform, as well as for implementing security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats.
Data Protection
Cloud providers are responsible for protecting customer data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure, as well as from accidental loss or destruction.
Customers are responsible for ensuring that their data is encrypted and that appropriate access controls are in place to protect it from unauthorized access.
Compliance
Cloud providers are responsible for ensuring that their cloud platforms and services comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Customers are responsible for ensuring that their use of the cloud platform and services complies with applicable laws and regulations, as well as with the cloud provider’s terms of service.
Cloud Architecture Design Principles for Compliance
Compliant cloud architecture is designed following fundamental principles that ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards. These principles encompass security measures, data management, and operational controls to protect sensitive information and maintain regulatory compliance.
Data Segregation
Data segregation involves logically or physically separating data based on sensitivity, classification, or regulatory requirements. This principle minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches by restricting access to specific individuals or systems.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms define who can access data, systems, and resources in the cloud environment. These mechanisms include authentication, authorization, and role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized users have access to the appropriate resources.
Encryption
Encryption is a critical principle for protecting data confidentiality. Data should be encrypted at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access or interception. Encryption keys should be securely managed and rotated regularly to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data.
Logging and Monitoring
Logging and monitoring systems are essential for detecting and responding to security incidents. These systems collect and analyze logs, events, and metrics from cloud resources to identify potential threats, suspicious activities, and compliance violations.
Incident Response
An incident response plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. This plan includes procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security breaches or compliance violations. Regular testing and updating of the incident response plan are crucial to ensure its effectiveness.
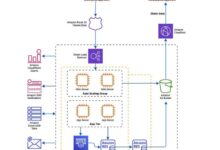
Compliance-Focused Cloud Architecture Diagrams
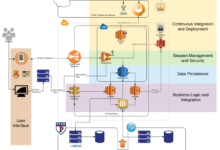
Cloud architecture diagrams for compliance visually depict the key components, data flows, and security controls required to meet specific compliance regulations and standards. They serve as valuable tools for communicating and documenting compliance-related design decisions, ensuring alignment with regulatory requirements.
Diagram Components
Compliance-focused cloud architecture diagrams typically include the following components:
- Cloud Service Provider (CSP) Infrastructure: Represents the underlying infrastructure provided by the CSP, such as compute, storage, and networking resources.
- Customer Resources: Depicts the customer’s workloads, applications, and data stored or processed in the cloud.
- Compliance Boundaries: Defines the scope of compliance, indicating which parts of the cloud architecture are subject to specific regulations or standards.
- Data Flows: Illustrates the movement of data between different components of the cloud architecture, including data transfers between on-premises and cloud environments.
- Security Controls: Shows the security measures implemented to protect data and systems, such as encryption, access control, and intrusion detection systems.
- Compliance Artifacts: Includes references to relevant compliance policies, procedures, and reports.
Data Protection and Privacy Considerations
Ensuring data protection and privacy is a fundamental aspect of cloud architecture for compliance. Organizations must prioritize safeguarding sensitive information and adhering to privacy regulations and standards. Effective data protection strategies are crucial for maintaining trust and preventing data breaches or unauthorized access.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a critical measure for protecting data confidentiality. Encrypting data renders it unreadable to unauthorized individuals, even if they gain access to it. Organizations can implement encryption at various levels, including storage, transmission, and processing. Encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, provide robust protection against unauthorized decryption attempts.
Data Masking
Data masking involves obscuring or replacing sensitive data with fictitious or synthetic values. This technique helps protect data privacy by preventing unauthorized individuals from accessing or interpreting confidential information. Data masking can be applied to various data types, including personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, and healthcare records.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms restrict access to data and resources based on predefined rules and permissions. Organizations can implement role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), or other access control models to ensure that only authorized users can access specific data or resources.
Access control policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to maintain appropriate levels of protection.
Regulatory Compliance Audits and Reporting
Regular compliance audits and transparent reporting are critical for organizations leveraging cloud services to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and maintain trust with stakeholders. These audits and reports provide a systematic approach to assess and document compliance efforts, enabling organizations to proactively identify and address any gaps or deviations from compliance standards.
Conducting Regular Compliance Audits
Implementing a comprehensive compliance audit program is essential for effective compliance management. Organizations should:
- Establish a clear audit schedule based on the organization’s risk profile and regulatory requirements.
- Define the scope and objectives of each audit, including the specific regulations or standards being assessed.
- Select qualified and independent auditors with expertise in the relevant compliance domains.
- Provide auditors with access to necessary documentation, systems, and personnel to facilitate a thorough review.
- Document audit findings, including any non-conformities or areas for improvement, along with corrective actions.
Documenting Findings and Reporting on Compliance Status
Organizations should maintain accurate and up-to-date records of compliance audits and findings. These records serve as evidence of compliance efforts and provide a basis for reporting to stakeholders. Compliance reports should:
- Summarize the audit findings, including any non-conformities or areas for improvement.
- Describe the corrective actions taken or planned to address non-conformities.
- Provide an overall assessment of the organization’s compliance status, including any certifications or accreditations obtained.
- Be communicated to relevant stakeholders, including management, regulatory bodies, and customers.
By conducting regular compliance audits and reporting on the findings, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to compliance, enhance transparency, and build trust with stakeholders. This proactive approach helps organizations maintain a compliant cloud environment, mitigate risks, and avoid potential legal or reputational consequences.
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance
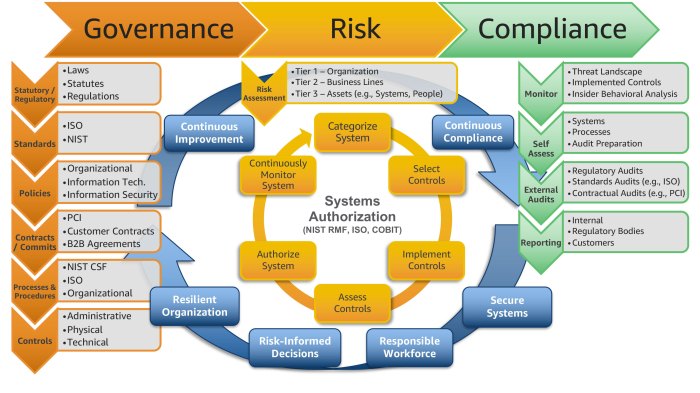
Maintaining continuous monitoring and compliance is crucial in cloud architecture to ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory standards and organizational policies. It involves actively tracking, detecting, and responding to security events, configuration changes, and compliance violations.
Implementing automated monitoring tools, logging systems, and incident response mechanisms is essential for effective compliance. These tools provide real-time visibility into cloud environments, allowing organizations to promptly identify and address potential risks or deviations from compliance requirements.
Automated Monitoring Tools
Deploying automated monitoring tools enables organizations to continuously assess their cloud infrastructure and applications for compliance. These tools can be configured to monitor various aspects, such as:
- Resource utilization and performance
- Security configurations and vulnerabilities
- Access control and authorization
- Compliance with industry standards and regulations
Logging Systems
Establishing comprehensive logging systems is essential for compliance. These systems collect and store detailed records of events, activities, and transactions occurring within the cloud environment. Logs provide valuable insights for:
- Identifying and investigating security incidents
- Troubleshooting issues and maintaining system stability
- Demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements
Incident Response Mechanisms
Having a well-defined incident response plan and associated mechanisms is crucial for effectively managing and mitigating compliance-related incidents. This plan should include:
- Clear roles and responsibilities for incident response
- Established communication channels and escalation procedures
- Processes for containment, eradication, and recovery from incidents
- Regular testing and updating of the incident response plan
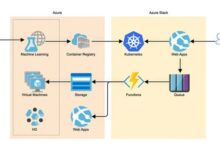
Cloud Compliance Frameworks and Tools
In the ever-changing landscape of cloud computing, organizations face the challenge of ensuring compliance with a myriad of regulations and standards. To address this, numerous cloud compliance frameworks and tools have emerged to assist organizations in their compliance efforts.
These frameworks and tools provide guidance, best practices, and automated solutions to help organizations achieve and maintain compliance in the cloud. By leveraging these resources, organizations can streamline their compliance processes, reduce risks, and demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
Popular Cloud Compliance Frameworks and Tools
- CIS Benchmarks: The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Benchmarks are a set of security configuration standards for various cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. These benchmarks provide detailed guidance on how to securely configure cloud resources to mitigate common security risks.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is a comprehensive framework that provides a set of best practices and guidelines for managing cybersecurity risks. It is widely used by organizations to assess and improve their cybersecurity posture, including their cloud environments.
- Azure Security Center: Azure Security Center is a cloud-native security management tool that provides comprehensive visibility, threat detection, and response capabilities for Azure resources. It helps organizations monitor and protect their cloud environments, detect and respond to security threats, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Using Cloud Compliance Frameworks and Tools
- Streamlined Compliance Processes: Cloud compliance frameworks and tools provide organizations with a structured approach to compliance, helping them streamline their compliance processes and reduce the time and effort required to achieve and maintain compliance.
- Reduced Risks: By following the guidance and best practices provided by these frameworks and tools, organizations can mitigate security risks and reduce the likelihood of compliance breaches. This helps protect their cloud environments, data, and applications from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and other threats.
- Demonstrated Adherence to Regulatory Requirements: Cloud compliance frameworks and tools help organizations demonstrate their adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards. This is essential for organizations that are subject to compliance regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI DSS, as it provides evidence of their commitment to data protection and security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud architecture diagrams for compliance serve as a critical tool for organizations to navigate the ever-changing landscape of regulatory requirements. By adhering to fundamental design principles, leveraging compliance frameworks and tools, and implementing continuous monitoring and reporting mechanisms, organizations can ensure the security and privacy of their data in the cloud, fostering trust among stakeholders and maintaining a competitive edge in the digital age.