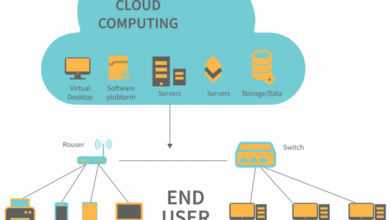
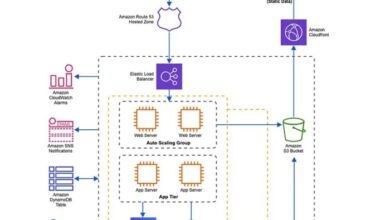
Cloud Architecture Diagrams: Guiding Your Cloud Migration Journey
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cloud migration has emerged as a pivotal strategy for businesses seeking agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, navigating the complexities of cloud migration requires a clear understanding of the underlying architecture. Enter cloud architecture diagrams—visual representations that serve as blueprints for your cloud migration journey, providing a comprehensive roadmap to guide your transition.
Cloud architecture diagrams offer a structured approach to planning, designing, and implementing your cloud migration strategy. These diagrams help visualize the intricate relationships between various cloud components, ensuring a seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructure. Dive into the world of cloud architecture diagrams and unlock the secrets to a successful cloud migration.
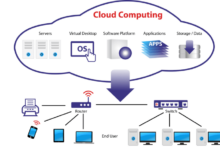
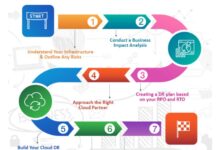
Cloud Migration Overview
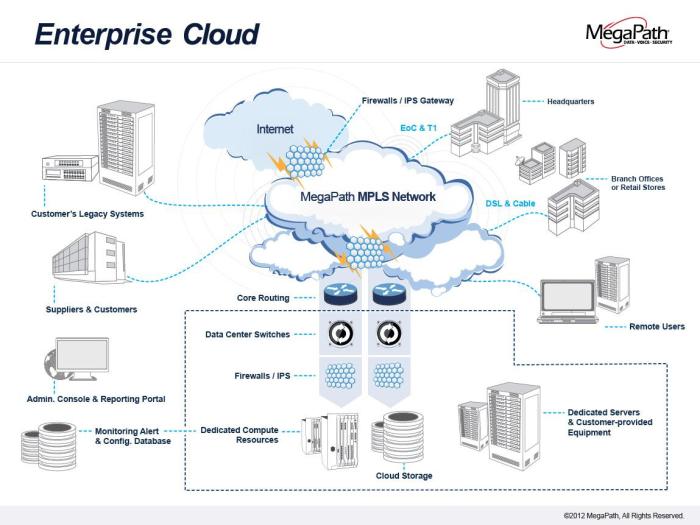
Cloud migration has revolutionized the modern IT landscape, offering businesses a transformative approach to their digital infrastructure. It involves moving applications, data, and other IT resources from on-premises data centers to cloud platforms, such as public, private, or hybrid clouds.
Cloud migration provides numerous benefits, including cost optimization, scalability, enhanced security, improved agility, and increased collaboration. However, it also poses challenges, such as managing data security and privacy, ensuring regulatory compliance, and dealing with potential downtime during the migration process.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
- Cost Optimization: Cloud migration can significantly reduce IT costs by eliminating the need for hardware maintenance, power consumption, and data center space. It also offers flexible pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go, which allows businesses to scale their cloud resources based on their actual usage.
- Scalability: Cloud platforms offer virtually limitless scalability, enabling businesses to quickly and easily scale their IT resources up or down to meet changing demands. This eliminates the need for costly hardware upgrades or capacity planning.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers typically invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, intrusion detection, and firewalls, to protect customer data and applications. This can provide a higher level of security compared to on-premises data centers.
- Improved Agility: Cloud migration enables businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands. With the cloud, businesses can easily deploy new applications, scale existing ones, and integrate with third-party services, accelerating innovation and time-to-market.
- Increased Collaboration: Cloud platforms facilitate collaboration among teams and departments, enabling real-time access to shared data and applications. This improves communication, productivity, and decision-making.
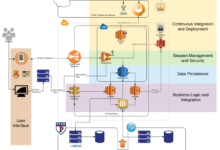
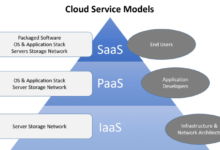
Cloud Architecture Diagrams
Cloud architecture diagrams are visual representations of the components and relationships within a cloud computing environment. They play a crucial role in cloud migration planning by providing a clear understanding of the existing IT infrastructure, the desired cloud architecture, and the steps required to transition from one to the other.
There are various types of cloud architecture diagrams, each serving a specific purpose. These include:
Logical Diagrams
Logical diagrams depict the high-level components and their interconnections within a cloud architecture. They provide an abstract view of the system, focusing on the functional relationships and dependencies between components, without delving into the physical details.
Physical Diagrams
Physical diagrams, also known as infrastructure diagrams, illustrate the physical components of a cloud architecture, such as servers, storage devices, network infrastructure, and their physical connections. These diagrams help visualize the physical layout and connectivity of the cloud environment.
Hybrid Diagrams
Hybrid diagrams combine elements of both logical and physical diagrams, providing a comprehensive representation of a cloud architecture. They depict the logical components and their interconnections, as well as the physical infrastructure on which they reside. Hybrid diagrams offer a holistic view of the cloud environment, encompassing both the abstract and physical aspects.
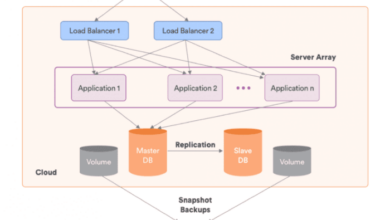
Components of Cloud Architecture Diagrams
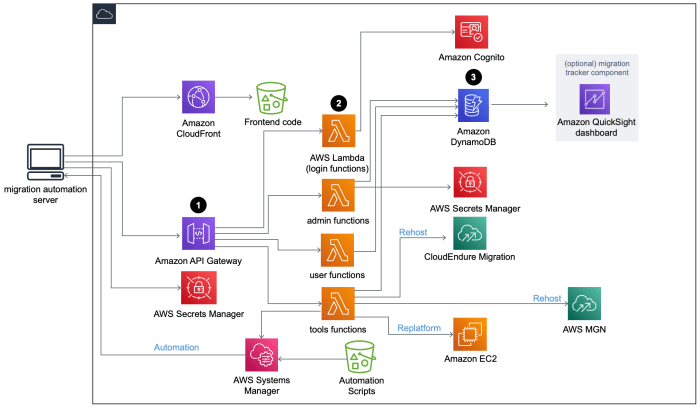
Cloud architecture diagrams are visual representations of the components and relationships within a cloud-based system. These diagrams provide a comprehensive overview of the system’s architecture, making it easier to understand its structure, functionality, and interactions.
Key components typically included in cloud architecture diagrams include:
Cloud Providers
Cloud providers are entities that offer cloud computing services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). They provide the infrastructure, platforms, and tools necessary for businesses to deploy and manage applications and data in the cloud.
Data Centers
Data centers are physical facilities that house the servers, storage systems, and other equipment necessary for cloud computing. They provide the physical infrastructure for cloud providers to operate their services.
Networks
Networks are the communication channels that connect the various components of a cloud architecture. They enable data to flow between cloud providers, data centers, and applications.
Applications
Applications are the software programs that run on cloud infrastructure. They can be developed and deployed by businesses or obtained from third-party providers.
Relationships and Interactions
The components of a cloud architecture diagram interact with each other in various ways to provide cloud computing services. Cloud providers offer a range of services, such as compute, storage, and networking, which are delivered through data centers and networks.
Applications are deployed on cloud infrastructure and interact with cloud services to perform various tasks.
Creating Cloud Architecture Diagrams
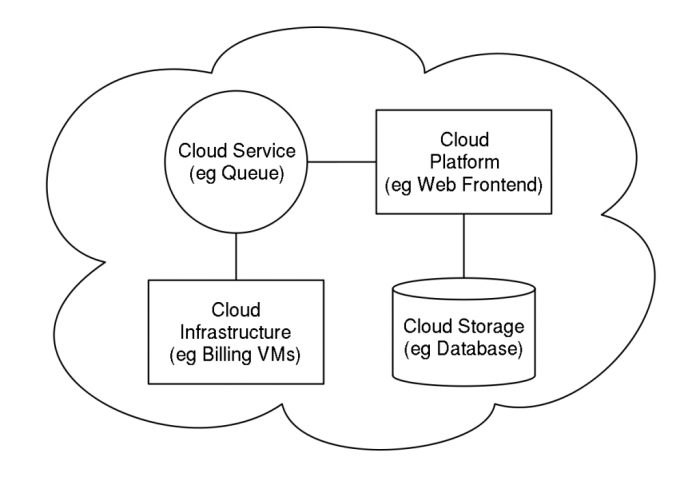
Creating cloud architecture diagrams is a crucial step in the cloud migration process, enabling stakeholders to visualize and understand the proposed cloud environment. It involves gathering requirements, selecting appropriate tools, and documenting the architecture in a clear and concise manner.
Step-by-Step Process
Follow these steps to create effective cloud architecture diagrams:
- Gather Requirements:
- Identify stakeholders and their needs.
- Understand the current IT environment and applications.
- Define the scope and objectives of the cloud migration.
- Select Appropriate Tools:
- Consider factors like complexity, scale, and stakeholder needs.
- Choose a tool that supports collaboration and integration with other tools.
- Ensure the tool can generate diagrams in various formats.
- Document the Architecture:
- Create a logical diagram depicting the overall architecture.
- Develop physical diagrams showing the infrastructure components.
- Include detailed descriptions, annotations, and legends.
- Review and Iterate:
- Share the diagrams with stakeholders for feedback.
- Refine and iterate the diagrams based on feedback.
- Ensure the diagrams remain up-to-date with changes in the architecture.
Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the right cloud architecture diagram tool is crucial for effective diagram creation. Consider the following factors:
- Complexity: Choose a tool that can handle the complexity of your cloud architecture.
- Scale: Ensure the tool can support the scale of your cloud environment.
- Stakeholder Needs: Consider the needs of different stakeholders, such as technical architects, business leaders, and end-users.
- Collaboration: Select a tool that supports collaboration among team members.
- Integration: Choose a tool that integrates with other tools in your IT ecosystem.
- Diagram Formats: Ensure the tool can generate diagrams in various formats, such as PNG, JPG, and SVG.
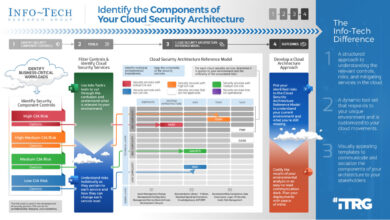
Best Practices for Cloud Architecture Diagrams
Creating effective cloud architecture diagrams requires careful consideration of clarity, consistency, and adherence to industry standards. These diagrams serve as visual representations of complex cloud environments, enabling stakeholders to understand the architecture, identify dependencies, and make informed decisions.
Clarity and Simplicity
- Use clear and concise language that is easily understood by both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Avoid unnecessary details and focus on the most important aspects of the architecture.
- Organize the diagram logically, grouping related components together and using consistent spacing and alignment.
Consistency and Standards
- Follow industry-standard symbols and notations to ensure that the diagram is easily understood by a wide range of stakeholders.
- Use consistent colors, shapes, and fonts throughout the diagram to enhance readability and understanding.
- Maintain consistency in the level of detail provided across different parts of the diagram.
Visual Elements
- Incorporate visual elements such as colors, shapes, and icons to enhance the readability and understanding of the diagram.
- Use colors to differentiate between different components or layers of the architecture.
- Use shapes to represent different types of components, such as servers, databases, and networks.
- Use icons to represent specific services or functions within the cloud environment.
Collaboration and Feedback
- Involve stakeholders in the creation and review of the cloud architecture diagram to ensure that it meets their needs and accurately reflects the intended architecture.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders throughout the process to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the final diagram is clear, accurate, and useful.
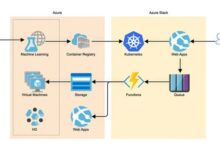
Cloud Migration Scenarios and Examples
Cloud migration is a complex process involving various scenarios and objectives. Cloud architecture diagrams play a crucial role in visualizing and planning the migration journey, helping stakeholders understand the migration approach, potential challenges, and expected outcomes.
Migration Scenarios and Corresponding Cloud Architecture Diagrams
The following table presents different cloud migration scenarios, their objectives, potential challenges, and corresponding cloud architecture diagrams:
| Scenario | Objectives | Challenges | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lift and Shift | Rapidly migrate existing applications and infrastructure to the cloud with minimal changes. | Potential compatibility issues, performance degradation, and security concerns. | Link to Lift and Shift Diagram |
| Re-platforming | Modernize applications by migrating them to a different cloud platform while retaining their core functionality. | Requires code refactoring, potential downtime, and integration challenges. | Link to Re-platforming Diagram |
| Re-architecting | Transform applications to fully leverage cloud-native services and architectures. | Requires significant code changes, potential performance risks, and the need for specialized expertise. | Link to Re-architecting Diagram |
| Greenfield Development | Build new applications from scratch in the cloud, leveraging cloud-native technologies and services. | Requires careful planning, architectural design, and security considerations. | Link to Greenfield Development Diagram |
Key Considerations:
Scenario Selection
Choosing the appropriate migration scenario depends on factors such as application complexity, budget, timeline, and business requirements.
Cloud Architecture Diagrams
Visualizing the migration process using cloud architecture diagrams helps identify dependencies, potential bottlenecks, and areas for optimization.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective communication among stakeholders is crucial to ensure a smooth migration process. Cloud architecture diagrams facilitate shared understanding and decision-making.
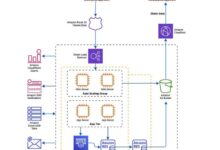
Case Studies and Success Stories
Cloud architecture diagrams play a crucial role in facilitating smooth and successful cloud migrations. To illustrate their significance, let’s explore real-world case studies and success stories of organizations that have leveraged cloud architecture diagrams to achieve effective cloud migrations.
Migrating a Legacy Application to the Cloud: A Manufacturing Company’s Journey
A manufacturing company faced the challenge of migrating its legacy application, which was running on an outdated infrastructure, to the cloud. The company’s IT team utilized cloud architecture diagrams to map out the existing application architecture, identify dependencies, and plan the migration strategy.
The diagrams helped visualize the migration process, ensuring a seamless transition to the cloud while minimizing downtime and disruption to business operations.
Optimizing Cloud Costs: A Retail Company’s Approach
A retail company aimed to optimize its cloud costs by identifying and eliminating inefficiencies in its cloud infrastructure. The company’s cloud architects created detailed cloud architecture diagrams that provided a comprehensive view of the cloud resources being utilized. By analyzing the diagrams, the team identified areas where resources were underutilized or could be consolidated, leading to significant cost savings and improved resource allocation.
Achieving Scalability and Agility: A Healthcare Organization’s Transformation
A healthcare organization sought to enhance its scalability and agility to meet the growing demands for its digital services. The organization’s IT team employed cloud architecture diagrams to design a cloud-based infrastructure that could easily scale up or down based on patient needs and fluctuations in demand.
The diagrams enabled the team to visualize and plan for future growth, ensuring a responsive and adaptable cloud environment.
Last Recap
As you embark on your cloud migration journey, remember that cloud architecture diagrams are your trusted companions. They provide a clear roadmap, guiding you through the complexities of cloud migration. Embrace the power of visualization to optimize costs, enhance scalability, and strengthen security.
With cloud architecture diagrams as your guiding light, you can confidently navigate the ever-changing IT landscape, ensuring a smooth and successful transition to the cloud.